Augmented Reality in Schools: Merging the Physical and Digital Worlds
In the age of rapid technological advancement, the educational landscape is undergoing a seismic shift. Among the most promising developments is the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) in schools. This technology, which overlays digital information onto the real world, is revolutionizing the way students learn, interact, and perceive their surroundings. Let’s delve into the transformative potential of AR in education and how it’s bridging the gap between the physical and digital realms.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
At its core, AR is a technology that superimposes digital content—such as images, videos, sounds, or 3D models—onto the real world. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR) which immerses users in a completely virtual environment, AR enhances the real world by adding layers of digital information to it. This blending of the digital and physical worlds offers a unique experience, allowing users to interact with and manipulate digital elements in their real-world surroundings.
The origins of AR can be traced back to the 1960s, but it’s only in recent years, with the advent of smartphones and advanced computing, that it has become accessible to the general public. Today, with the proliferation of AR apps and tools, we’re witnessing its potential unfold across various sectors, including education.
The Benefits of AR in Education
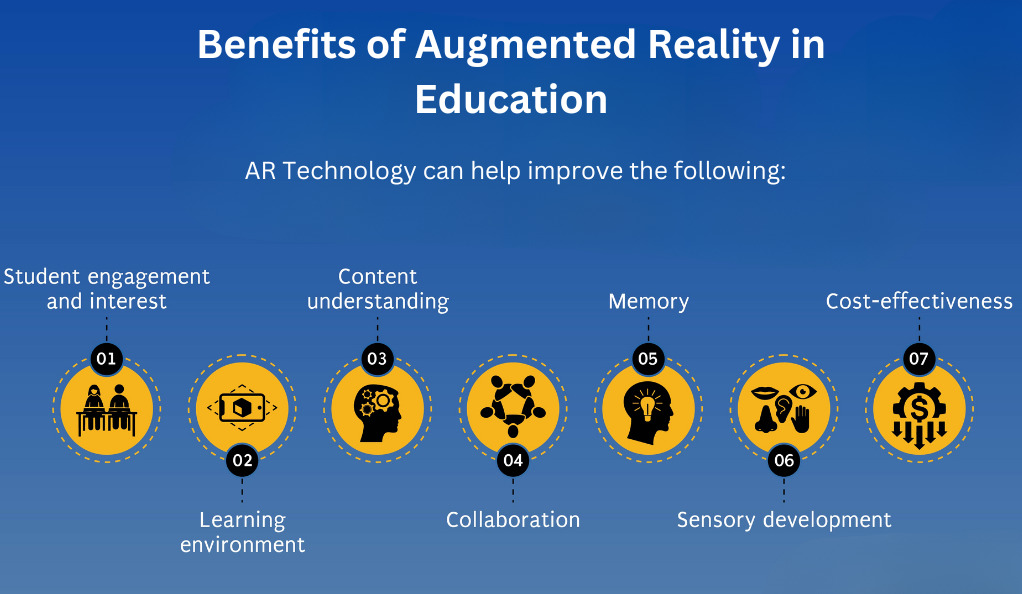
- Interactive Learning
AR transforms passive learning into an interactive experience. For instance, instead of merely reading about the solar system, students can use AR apps to visualize planets orbiting around the sun in their classroom. This hands-on approach not only enhances understanding but also fosters curiosity and exploration. - Enhanced Engagement
The immersive nature of AR captures students’ attention, making lessons more engaging and memorable. When students are actively involved in their learning process, they’re more likely to retain information and develop a genuine interest in the subject matter. - Accessibility
AR can make complex concepts more accessible. For example, visualizing a 3D model of a DNA strand can help students better understand its structure. This visual representation can be particularly beneficial for visual learners who might struggle with traditional text-based resources. - Real-world Application
AR can bridge the gap between theory and practice, allowing students to see the real-world application of what they’re learning. By contextualizing academic concepts, students can better appreciate their relevance and applicability.
AR in Action: Real-world Examples
- Historical Reconstructions
Imagine a history class where students can witness the construction of the pyramids or walk through ancient Rome. AR can bring historical events and places to life, providing a richer understanding of the past. This immersive experience can make history feel more tangible and relatable, breaking down the barriers of time and geography. - Science Experiments
Dangerous or intricate experiments can be safely demonstrated using AR, allowing students to explore without risks. For instance, chemical reactions that might be too hazardous for a school lab can be visualized using AR, ensuring safety while still offering a comprehensive learning experience. - Language Learning
AR apps can recognize objects and provide translations or pronunciations, aiding in vocabulary acquisition and language immersion. This real-time translation can be particularly useful for students traveling abroad or those trying to learn a language in a more contextual manner. - Field Trips
With AR, every classroom can become a potential field trip site. Students can explore underwater ecosystems or distant galaxies without ever leaving their seats. This virtual exploration can supplement traditional field trips, ensuring that learning isn’t confined by logistical constraints.
Challenges and Considerations
While AR offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to recognize its challenges:
- Equity and Access
Not all schools have the resources to implement AR technology. It’s crucial to ensure that advancements in education technology don’t widen the digital divide. Schools in underserved areas might lack the infrastructure or funding to integrate AR, potentially leaving some students behind. - Over-reliance
While AR is a powerful tool, it shouldn’t replace traditional teaching methods. A balanced approach ensures that students receive a well-rounded education. Teachers should be trained to use AR as a supplementary tool, ensuring that it enhances rather than replaces foundational teaching techniques. - Privacy Concerns
AR apps often require access to cameras and other sensors, raising concerns about student privacy and data security. Schools need to be vigilant about the apps and platforms they adopt, ensuring that student data is protected and that privacy standards are upheld.
The Future of AR in Schools
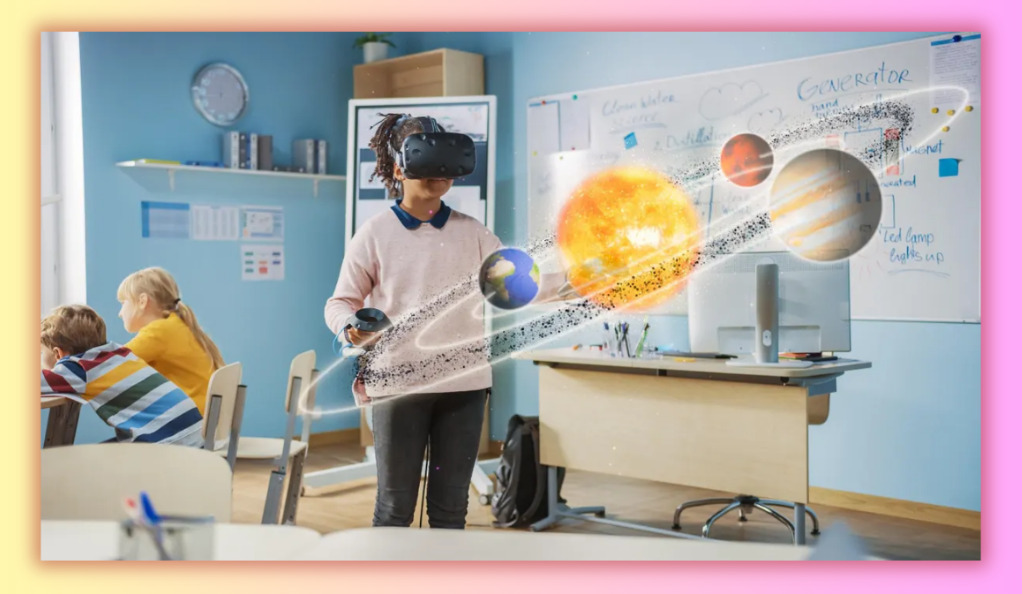

The potential of AR in education is vast. As technology becomes more affordable and accessible, we can expect to see a more widespread adoption of AR in classrooms worldwide. Future developments might include personalized AR learning experiences, collaborative AR projects, and even AR-enhanced textbooks. These innovations could redefine the boundaries of classroom learning, offering students a more holistic and immersive educational experience.
In conclusion, Augmented Reality is not just a technological novelty; it’s a transformative tool that can reshape the educational landscape. By merging the physical and digital worlds, AR offers a dynamic, engaging, and immersive learning experience, promising a brighter future for learners everywhere.
FAQs
While both AR and VR offer immersive experiences, they function differently. AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing what users see around them. In contrast, VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment, often requiring specialized headsets. In educational settings, AR might allow students to see a 3D model of a historical monument in their classroom, while VR might transport them to a virtual representation of ancient Rome.
Yes, there are a few considerations. Firstly, there’s the concern of equity and access; not all schools might have the resources to implement AR, potentially widening the digital divide. Secondly, over-reliance on AR could overshadow traditional teaching methods, which remain crucial. Lastly, there are privacy concerns, as AR apps often require access to cameras and other sensors, potentially compromising student data.
Educators should receive training on how to integrate AR tools into their lessons effectively. They should view AR as a supplementary tool that can enhance learning rather than replace foundational teaching techniques. Additionally, it’s essential to choose age-appropriate AR applications and ensure that the content aligns with curriculum goals.
While specialized AR glasses and headsets are available, many AR applications for education are designed for smartphones and tablets, devices that many students already have access to. However, the type of equipment needed will depend on the specific AR application or program being used.
Schools should be vigilant about the AR apps and platforms they adopt. It’s essential to choose platforms that prioritize user privacy and data security. Schools should also establish clear guidelines on data collection and storage, ensuring that any data captured through AR tools is protected and used ethically.
